For an explanation of why, read the digression above The concepts in there really are fundamental to understanding a lot of graphing Examples y=f(x) No translation y=f(x2) The 2 is grouped with the x, therefore it is a horizontal translation Since it is added to the x, rather than multiplied by the x, it is a shift and not a scaleC < 0 moves it downAlgebra Examples Popular Problems Algebra Graph y=f(x) Find the absolute value vertex In this case, the vertex for is Tap for more steps To find the coordinate of the vertex, set the inside of the absolute value equal to In this case, Replace the variable with in the expression

Graphing Psat Math
Y=f(x) graph examples
Y=f(x) graph examples-If (x, y) belongs to the set defining f, then y is the image of x under f, or the value of f applied to the argument x In the context of numbers in particular, one also says that y is the value of f for the value x of its variable, or, more concisely, that y is the value of f of x, denoted as y = f(x)Math Plotting Graph for y=f(x) in Javascript y=f(x) Plot the Graph by defining the function below You can also press F12 to code the function in the console



2
Graph_CoordinateSystem coordinatesystem{ /* xmin, xmax, xstep */ 01, 30f, 001f, /* ymin, ymax, ystep */ 10, 150f, 001fDefinition of Y = f (X) In this equation X represents the input of the process and Y the output of the procees and f the function of the variable X Y is the dependent output variable of a process It is used to monitor a process to see if it is out of control, orA math reflection flips a graph over the yaxis, and is of the form y = f (x) Other important transformations include vertical shifts, horizontal shifts and horizontal compression Let's talk about reflections Now recall how to reflect the graph y=f of x across the x axis
1 You are correct, given any function f ( x), you get the graph of f ( x ) by taking the graph of f, deleting the graph where x < 0, then reflecting the graph where x > 0 into the region you deleted To understand the answer described in your second paragraph, think of f ( x − 1 ) as g ( x − 1) where we define g as the new function gQuestion (1 Point) Use The Two Graphs Below To Answer The Following Questions G(x) Is The Graph Of Y =f(x) (a) The Graph Of Y Scaled Horizontally Scaled Vertically A And Choose The Scaling Factor Choose The Scaling Factor (b) Find An Equation For G(x) In Terms Of The Function F(x) For Example, G(x) 10f(9x 8) 7 G(x) = Help (formulas) Yg) 6 6 5 5 3 2 15 1 Answer1 The graphs in the pictures are correct You have to interpret y = f ( x) and y = f ( x) as relations between real numbers These relations can be graphed in the plane They are different relations, as the pictures show When f ( x) < 0, there are no points ( x, y) such that y = f ( x)
Then the graph of y = f(x c) is obtained by translating the graph of y = f(x) c units to the right;Remember f(x) reflects any part of the original f(x) graph that was below the xaxis in the xaxis In this video I show you how to draw graphs of the form y=f(x) using the modulus function and give you three graphs to try Examples in the video Sketch the following yY = f (x) Process Outcome a Result of Process Inputs The mathematical term Y = f (x), which translates as simply " Y is a function of x," illustrates the idea that the important process outcomes ( Y s) are a result of the drivers ( x 's) within processes The goal of DMAIC is to identify which few process and input variables mainly




Average Rate Of Change Review Article Khan Academy




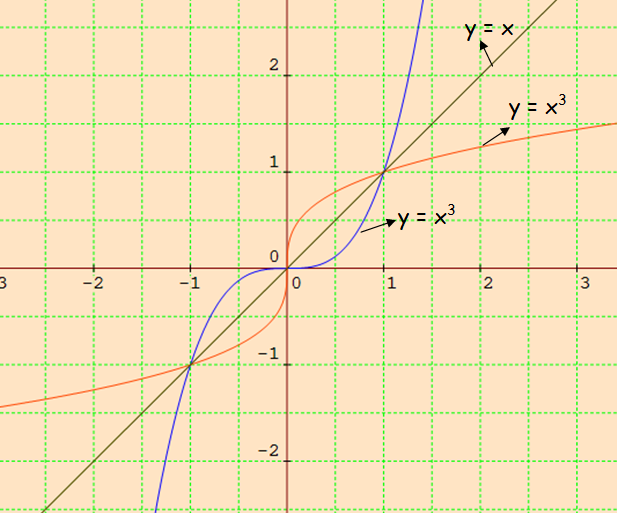
Graph Of Y X And Y F X In Example 9 Download Scientific Diagram
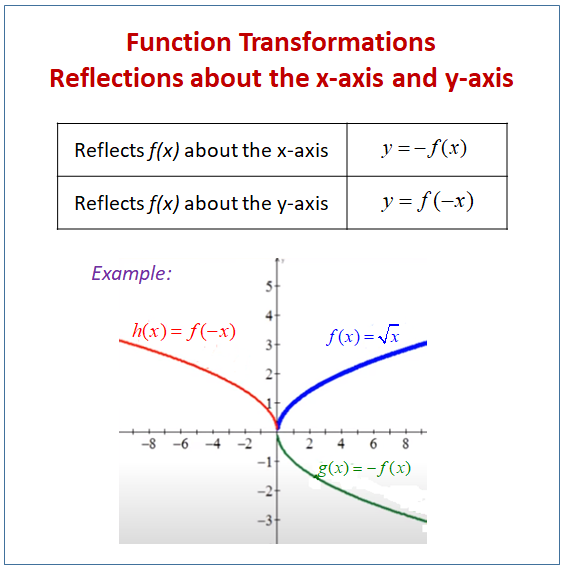
The graph of y = f (x) is the graph of y = f (x) reflected about the yaxis Here is a picture of the graph of g(x) =(05x)31 It is obtained from the graph of f(x) = 05x31 by reflecting it in the yaxis Summary of Transformations To graph Draw the graph of f and Changes in the equation of y = f(x) Vertical Shifts y = f (x) cReflection of Graph The graph of a given function can be reflected around {eq}x {/eq}axis (vertically) and {eq}y {/eq}axis (horizontally) If the function is given as {eq}y = f\left( x \rightExamples • The graph of f(x)=x2 is a graph that we know how to draw It's drawn on page 59 We can use this graph that we know and the chart above to draw f(x)2, f(x) 2, 2f(x), 1 2f(x), and f(x) Or to write the previous five functions




An Example Of A Strictly Concave Scalar Function Y F X Download Scientific Diagram



Operations On Functions Stretches And Shrinks Sparknotes
Graph of z = f(x,y) Discover Resources Shifting and Scaling logarithmic Graphs;Next, pick points between these designated xvalues and substitute them into the equation for f' to determine the sign ( or ) for each of these intervals Beneath each designated xvalue, write the corresponding yvalue which is found by using the original equation y = f(x) These ordered pairs (x, y) will be a starting point for the graphGraph Transformation Y F X A Of The Function F X Youtube For more information and source, see on this link https//myoutubecom/watch?v=gh9mOp9PQ3s



Horizontal And Vertical Graph Stretches And Compressions Video Lessons Examples And Solutions



Compress Or Stretch Function Horizontally F Cx Expii
The x1 you might think shifts the graph to the left but it shifts it to the right So let's just review really quickly what this transformation does y equals half of x xh is a horizontal shift If each is positive it shifts the graph to the right Like when h was one, we had x1 the graph was shifted to the right one unitTranslations of Functions Suppose that y = f(x) is a function and c > 0; 4 The Graph of a Function The graph of a function is the set of all points whose coordinates (x, y) satisfy the function `y = f(x)` This means that for each xvalue there is a corresponding yvalue which is obtained when we substitute into the expression for `f(x)` Since there is no limit to the possible number of points for the graph of the function, we will follow this




Graphing Psat Math



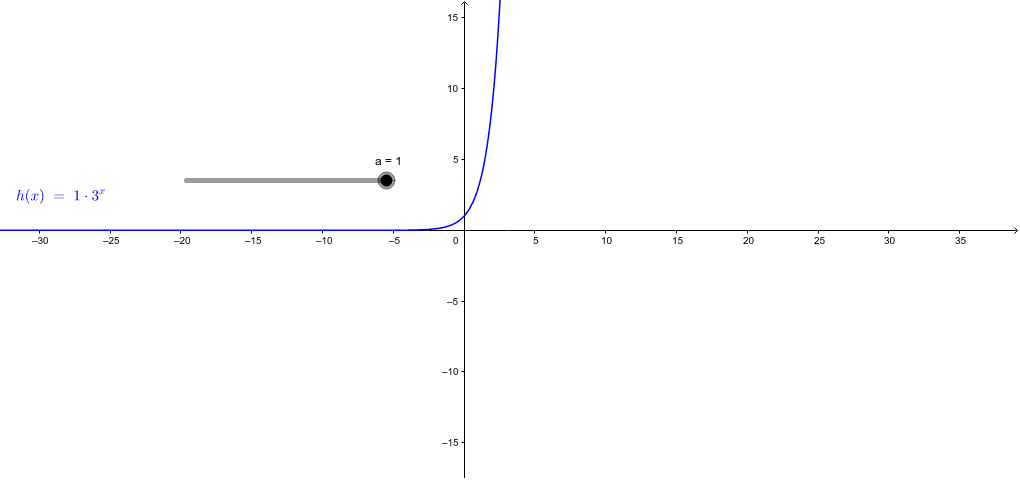
Introduction To Exponential Functions
We can derive properties of the graph of y = f 1(x) from properties of the graph of y = f(x), since they are refections of each other in the line y = x For example Theorem If f is a onetoone continuous function de ned on an interval, then its inverse f 1 is also onetoone and continuousShifting Of Graphs Transformation Example 1 Y F X Kup K Units Y F X Kdown K Units Vertical Shifting Below Is The Graph Of A Function Y Ppt DownloadIn our example above, x is the independent variable and y is the dependent variable A function is an equation that has only one answer for y for every x A function assigns exactly one output to each input of a specified type It is common to name a function either f(x) or g(x) instead of y f(2) means that we should find the value of our



2



Biomath Transformation Of Graphs
Another way to identify the domain and range of functions is by using graphs Because the domain refers to the set of possible input values, the domain of a graph consists of all the input values shown on the latexx/latexaxis The range is the set of possible output values, which are shown on the latexy/latexaxisDepends on context In mathematics, Y is often used to represent the vertical axis of a graph In this context, f(x) is a function that takes a parameter x and returns a value A function is similar to a series of steps You give it a number and i Simply put, the Y=f(x) equation calculates the dependent output of a process given different inputs Here's an example of some possible values for the variables in the "breakthrough equation" In a marketing context, the outcome (Y) could equal the number of product sales, where the function (f) could be email opens from a newsletter
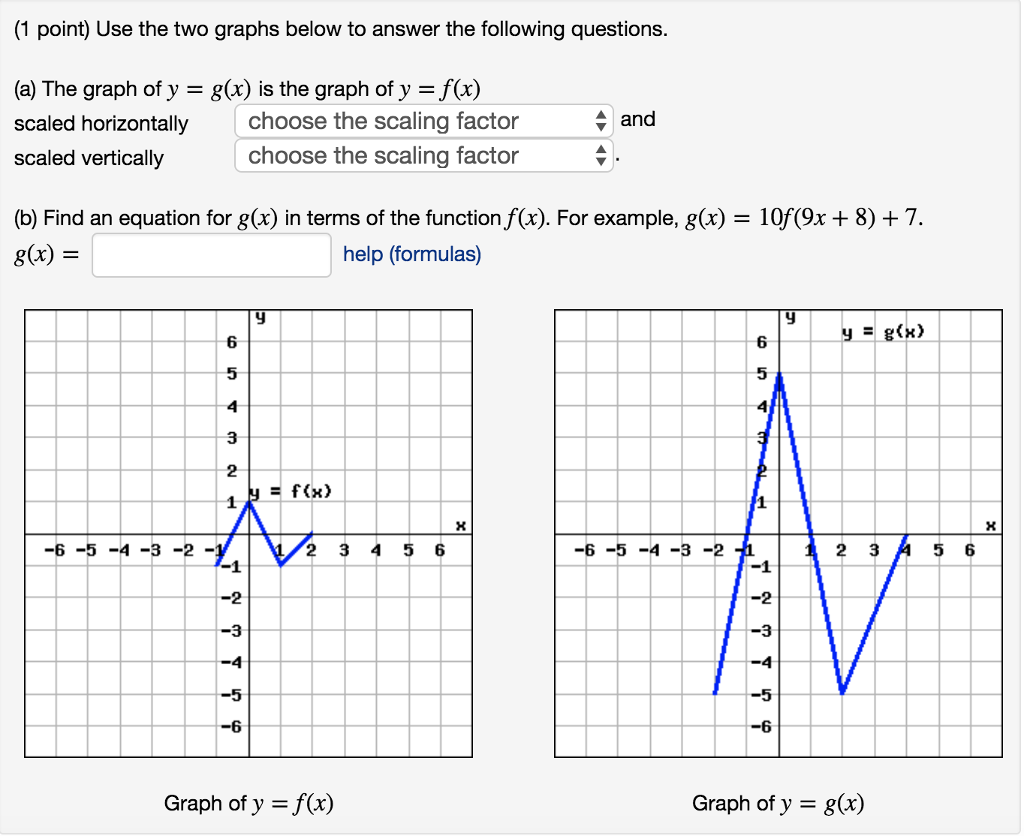



1 Point Use The Two Graphs Below To Answer The Chegg Com



1
The Graph of the Equation y = f (x) Examples, solutions, and videos to help Algebra I students learn how to understand the meaning of the graph of y = f (x), namely { (x, y) x ∈ D and y = f (x)} Students understand the definitions of when a function is increasing or decreasingMAFS912AREI411 Explain why the xcoordinates of the points where the graphs of the equations y = f(x) and y = g(x) intersect are the solutions of the equation f(x) = g(x);The graph of y = f(x c) is obtained by translating the graph of y = f(x) c units to the left;
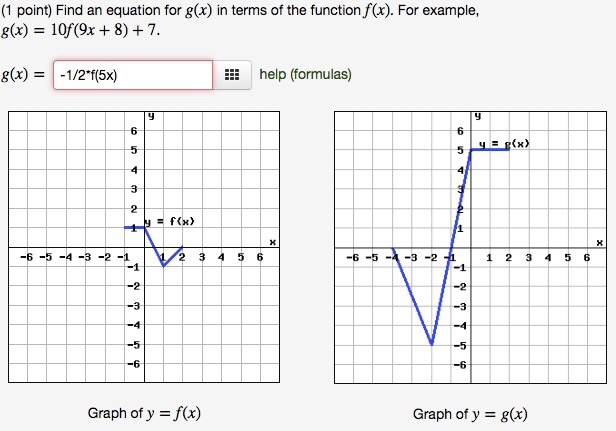



Solved 1 Point Find An Equation For G X In Terms Of Th Chegg Com
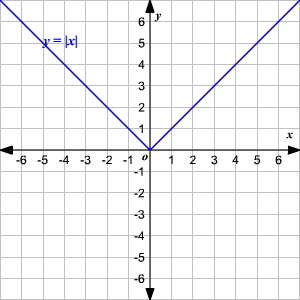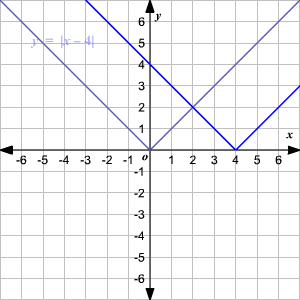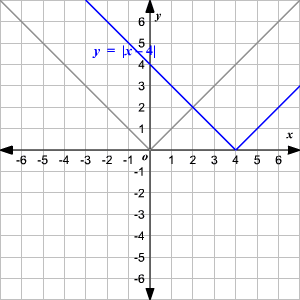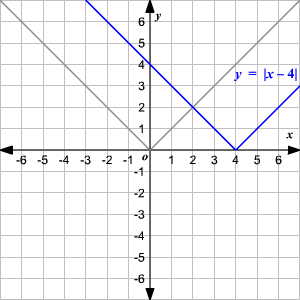



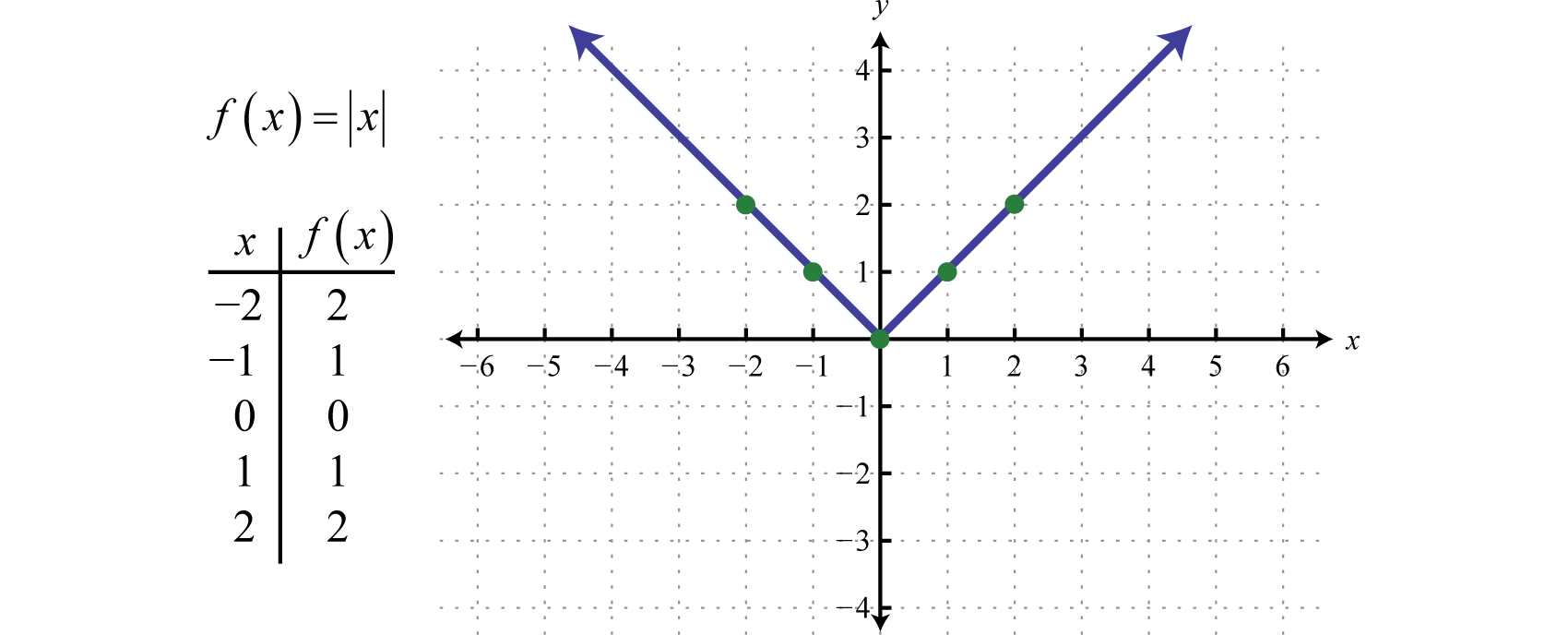
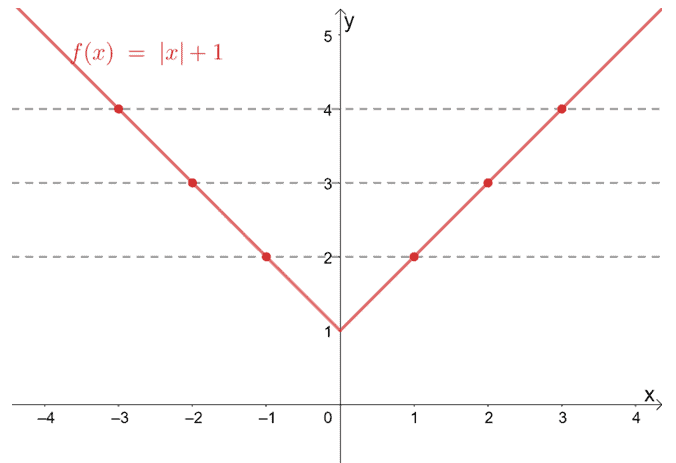
Absolute Value Functions
Let us consider the function {eq}y=f(x) {/eq} To shift the graph of the function vertically up or down in {eq}k {/eq} units we add or subtract the given value from the function, ie,Example We have a function \(y = f(x)\) We have multiplied the function with 2, ie, \y = 2f(x)\ We get, The distance of the points on the curve gets farther away from the xaxis The shape of the curve depends on the value of C If C > 1, the graph stretches and makes the graph steeper If C < 1, the graph shrinks and makes the graph flatterExample 1 Graph the logarithmic function f(x) = log 2 x and state range and domain of the function Solution Obviously, a logarithmic function must have the domain and range of (0, infinity) and (−infinity, infinity) Since the function f(x) = log 2 x is greater than 1, we will increase our curve from left to right, a shown below
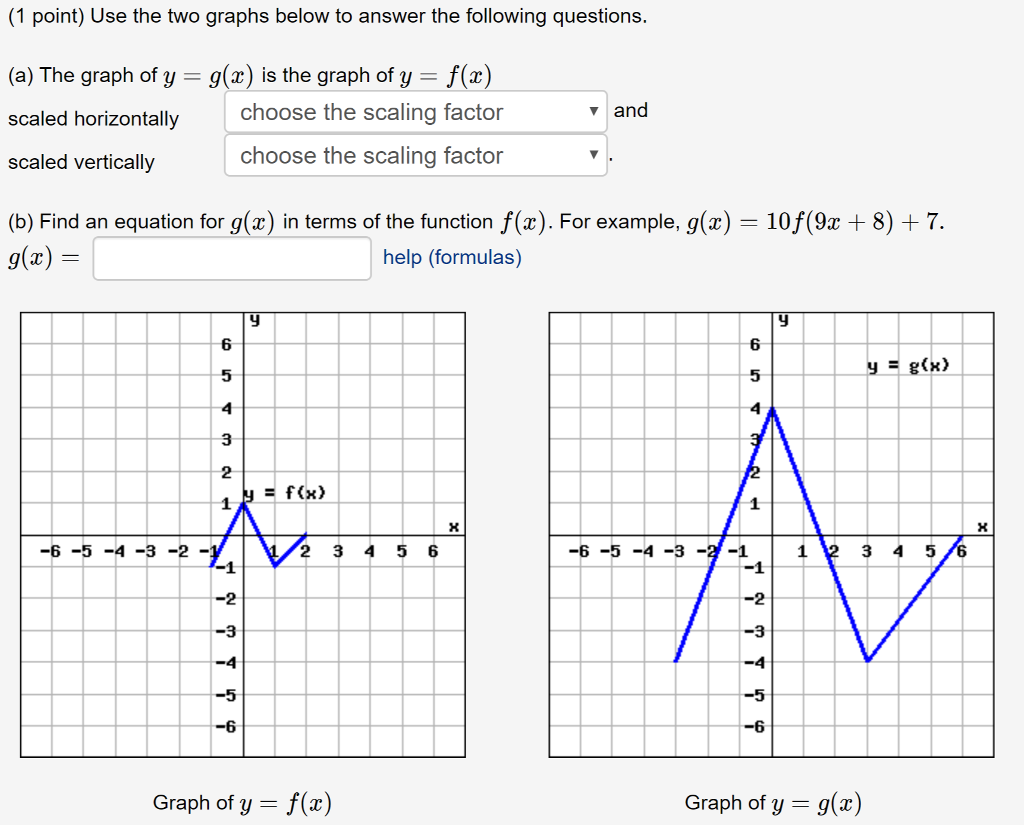



1 Point Use The Two Graphs Below To Answer The Chegg Com




Surjective Function Wikipedia
I am a graduate student teaching college algebra at a larger state school, and currently I'm covering transformations of graphs of function, ieTwo examples of reflecting a basic graph Two examples of reflecting a basic graphExample 1 Find the x and the y intercepts of the graph of function f defined by f(x) = 3 x 9 Solution to Example 1 Since a point on the y axis has x coordinate equal to zero, to find the y interecpt, we set x to zero and find the y coordinate which is f(0) f(0) = 3(0) 9 = 9 A point on the x axis has y coordinate equal to 0, to find the x intercept, we set y = f(x) = 0 and solve for x



Graphing Reflections Y F X Or Y F X Youtube



Identity Function Definition Graph Examples
The graph of a function f is the set of all points in the plane of the form (x, f(x)) We could also define the graph of f to be the graph of the equation y = f(x) So, the graph of a function if a special case of the graph of an equation Example 1 Let f(x) = x 2 3The most common graphs name the input value x x and the output value y y, and we say y y is a function of x x, or y = f (x) y = f ( x) when the function is named f f The graph of the function is the set of all points (x,y) ( x, y) in the plane that satisfies the equation y= f (x) y = f ( x) If the function is defined for only a few inputFree math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor



Www Math Utah Edu Wortman 1050 Text If Pdf
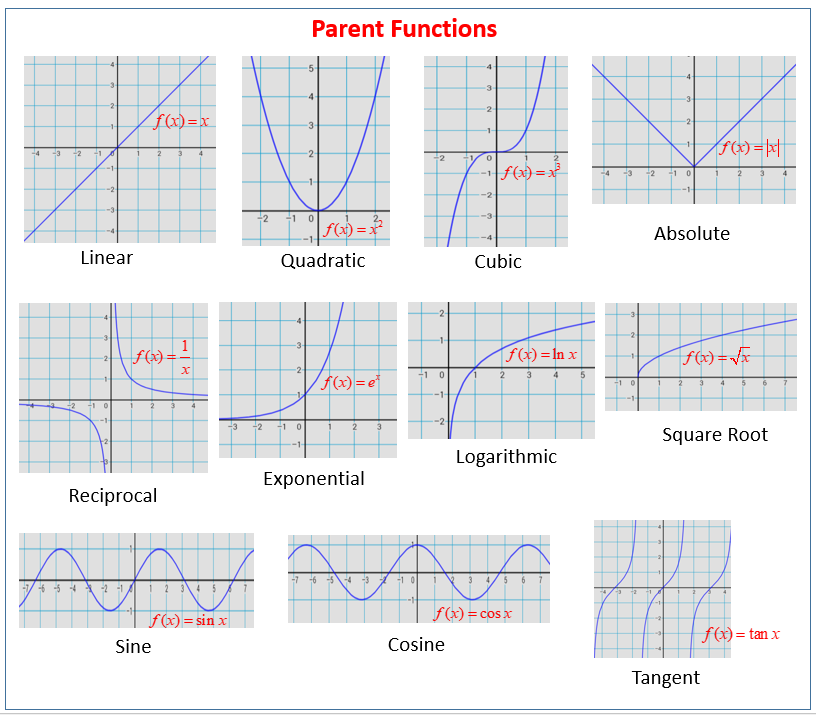



Parent Functions And Their Graphs Video Lessons Examples And Solutions
(x,y,0) in D along the z axis to the point (x,y,f(x,y)) Right The graph of the function studied in Example 163 useful picture of the behavior of the function The idea can be extended to functions of two variables Definition 162 (Graph of a Function of Two Variables) The graph of a function f(x,y) with domain D is a collection of pointsExample 1 Graph the point (4, 3) The first number in the parentheses, aka the x value, is 4 This is how far we go horizontally, on the x axis, from (0, 0) Because it's negative, we go left We don't put a point there yet, though We still need to moveA point P on the graph of y = f(x) is a point of inflection if f is continuous at P and the concavity of the graph changes at P In view of the above theorem, there is a point of inflection whenever the second derivative changes sign Example 3
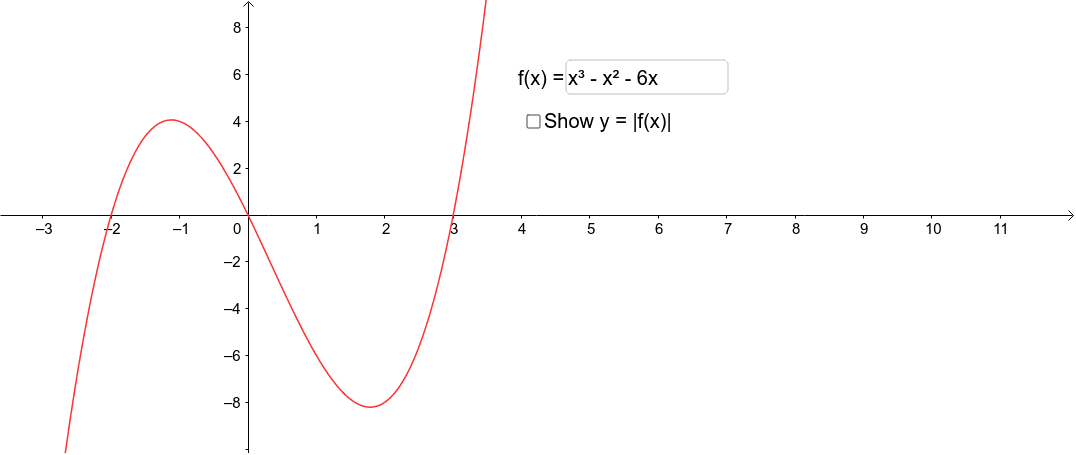



The Graph Of Y F X Geogebra



Transformations Mrs F X
Let us start with a function, in this case it is f(x) = x 2, but it could be anything f(x) = x 2 Here are some simple things we can do to move or scale it on the graph We can move it up or down by adding a constant to the yvalue g(x) = x 2 C Note to move the line down, we use a negative value for C C > 0 moves it up;Linear functions have the form f(x) = ax b, where a and b are constants In Figure 111, we see examples of linear functions when a is positive, negative, and zero Note that if a > 0, the graph of the line rises as x increases In other words, f(x) = ax b is increasing on ( − ∞, ∞)The equation For example the graph of the equation x2 y2 = 1 is the unit circle (circle of radius 1 centered at the origin)10 05 05 05 10 x 2y =1 If we can solve for y uniquely in terms of x in the given equation, we can rearrange the equation to look like y = f(x) for some function of x
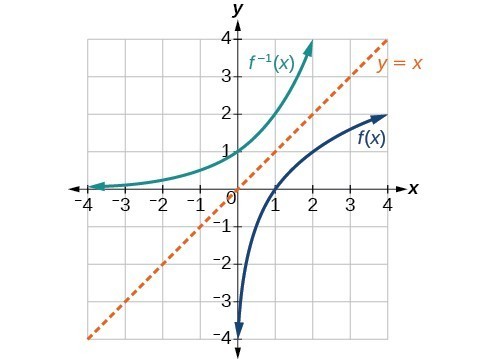



Use The Graph Of A Function To Graph Its Inverse College Algebra
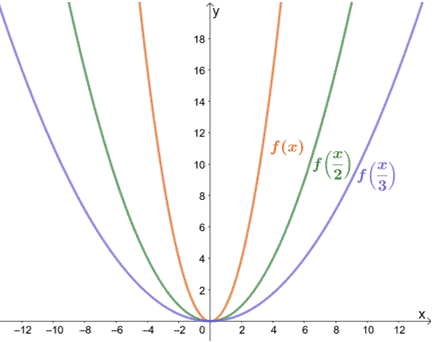



Horizontal Stretch Properties Graph Examples
Function Transformations Horizontal And Vertical Stretches And Compressions This video explains to graph graph horizontal and vertical stretches and compressions in the form a*f (b (xc))d This video looks at how a and b affect the graph of f (x) af (x) a > 1, stretch f (xFrom the graph of f ' (x), draw a graph of f(x) f ' is negative, then zero, then positive This means f will be decreasing for a bit, and will then turn around and increase We just don't know exactly where the graph of f(x) will be in relation to the yaxisWe can figure out the general shape of f, but f we could take the graph of f that we just made and shift it up or down along the y(ii) The graph y = f(−x) is the reflection of the graph of f about the yaxis (iii) The graph of y = f −1 (x) is the reflection of the graph of f in y = x Translation A translation of a graph is a vertical or horizontal shift of the graph that produces congruent graphs The graph of y = f(x c), c > 0 causes the shift to the left y
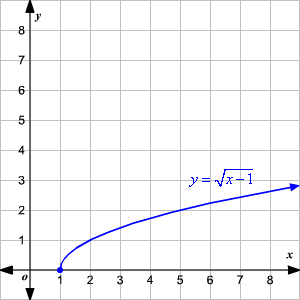



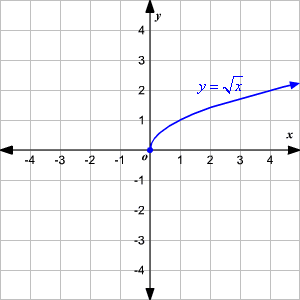
Graphing Square Root Functions



1 5 Shifting Reflecting And Stretching Graphs
Two examples are shown The first is a reflection across the xaxis and the second is a reflection across the yaxisThe graph of y = f(x) c is obtained by translating the graph of y = f(x) c units upwards; y=f(x) will indicate that the graph has reflected about the origin If I have f(x)=(x) 3 , then the graph would be reflected about the yaxis Try to experiment on these transformations by using a graphing utility such as Desmos , Symbolab , GeoGebra



Discontinuous Functions



Functions And Linear Equations Algebra 2 How To Graph Functions And Linear Equations Mathplanet
Find the solutions approximately, eg, using technology to graph the functions, make tables of values, or find successive approximationsInclude cases where f(x) and/or g(x) are linear, polynomial,




Answered 0 2 2 2 2 2 2 E D F 2 Bartleby
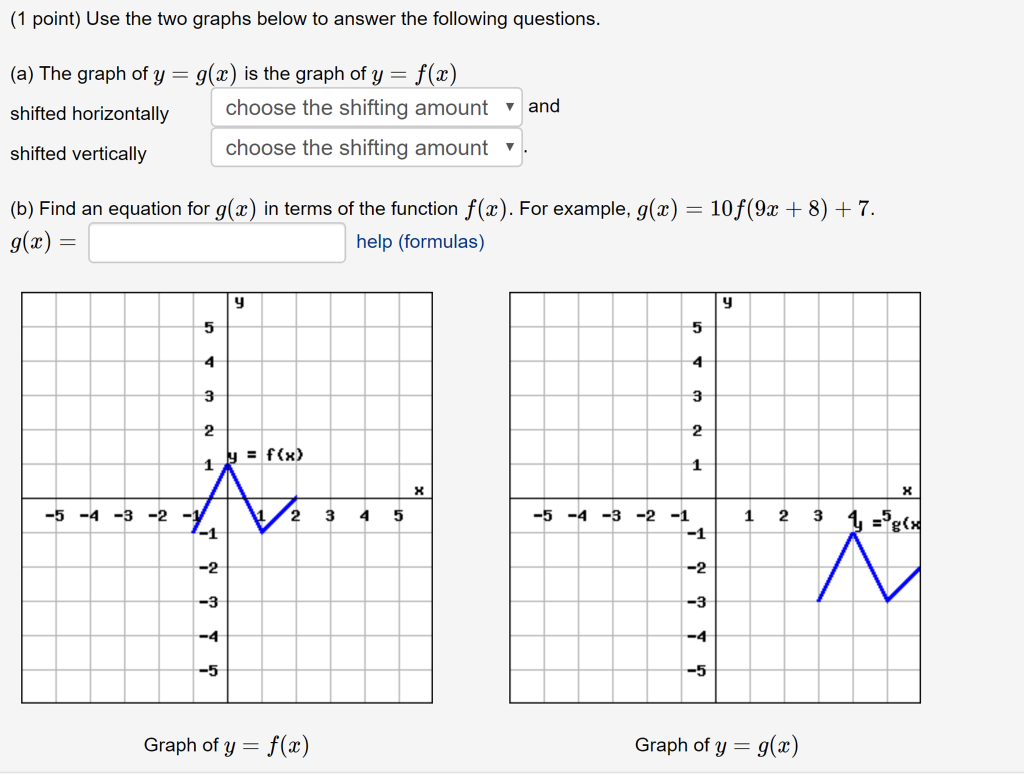



1 Point Use The Two Graphs Below To Answer The Chegg Com




Common Functions Reference



Graphing The Basic Functions



Graphs Of Y F X And Y F X Geogebra



Asymptote



Reflecting Functions Or Graphs Examples Solutions Worksheets Videos Games Activities




Vertical And Horizontal Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation



Graphing Square Root Functions



Sat Math Graph Example 2 Sat Math Forbest Academy



If The Minimum Point On The Graph Of The Equation Y F X Is 1 3 What Is The Minimum Point On He Graph Of The Equation Y F X 5 How Would I Go Enotes Com
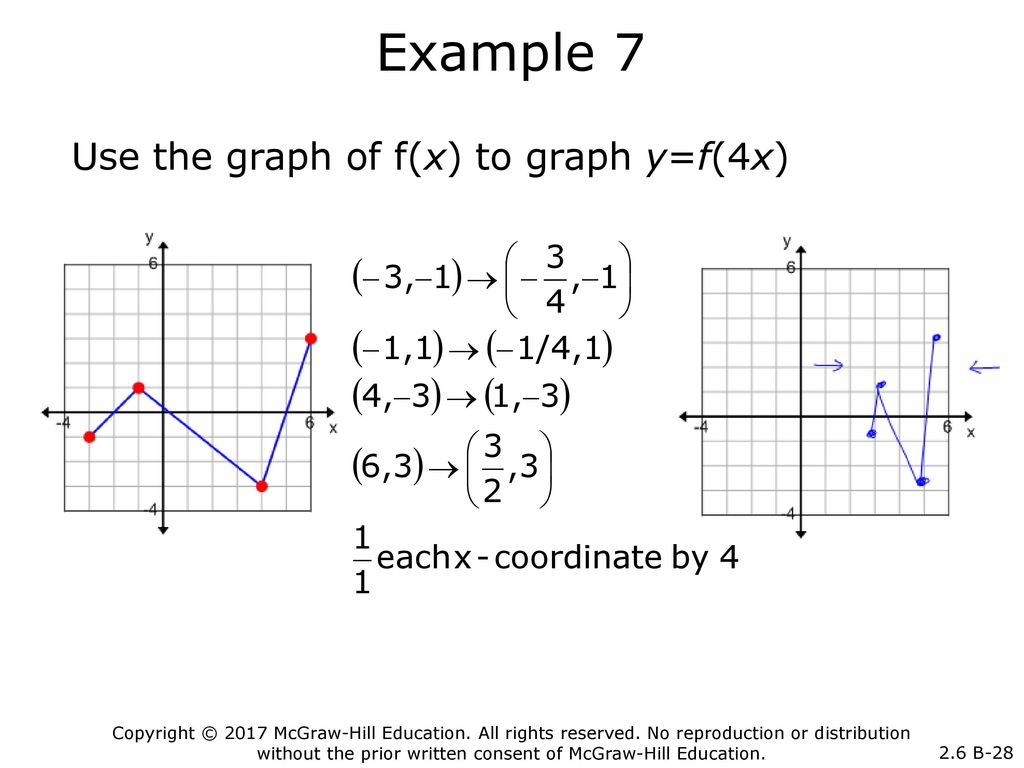



College Algebra Chapter 2 Functions And Graphs Ppt Download




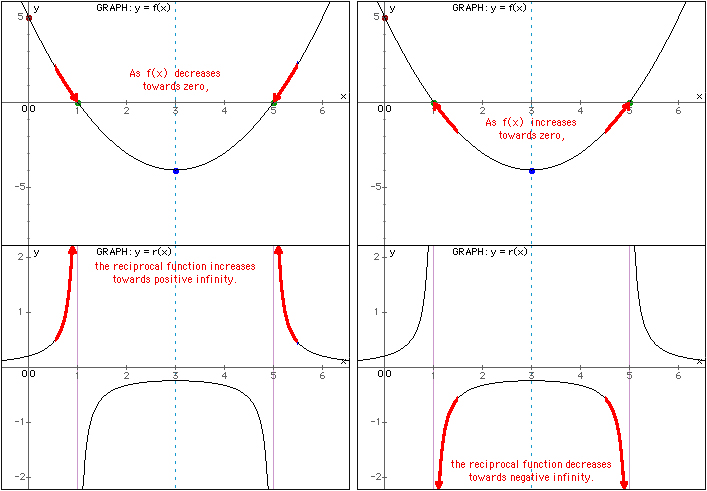
Draw Graph Of Frac 1 F X From Graph Of F X Mathematics Stack Exchange




3 5 Transformations Of Graphs Graph Functions Using
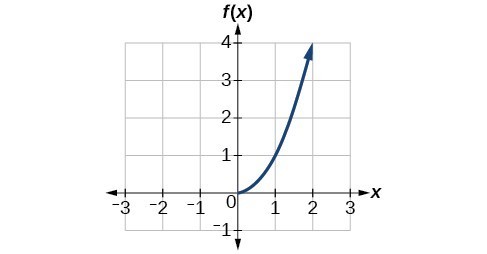



Use The Graph Of A Function To Graph Its Inverse College Algebra




Shifting Of Graphs Transformation Example 1 Y F X Kup K Units Y F X Kdown K Units Vertical Shifting Below Is The Graph Of A Function Y Ppt Download
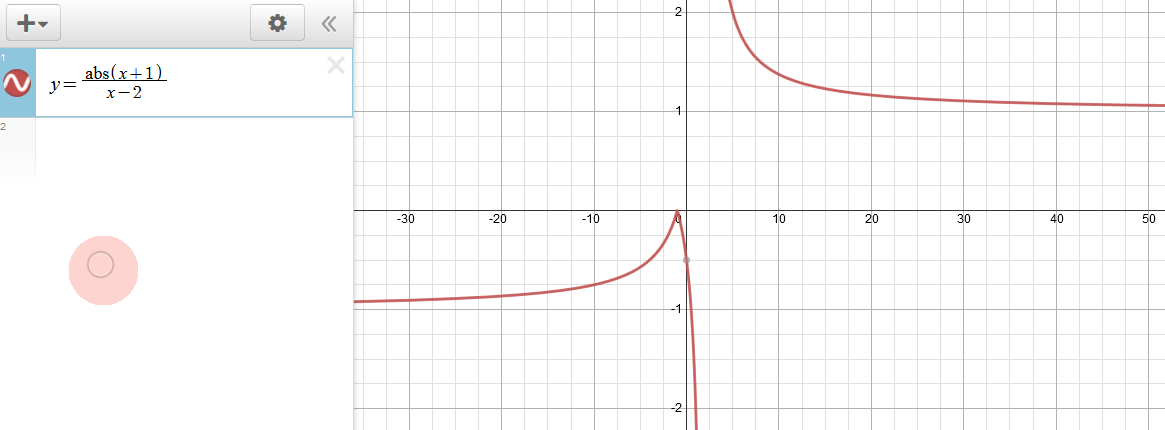



How Many Horizontal Asymptotes Can The Graph Of Y F X Have Socratic
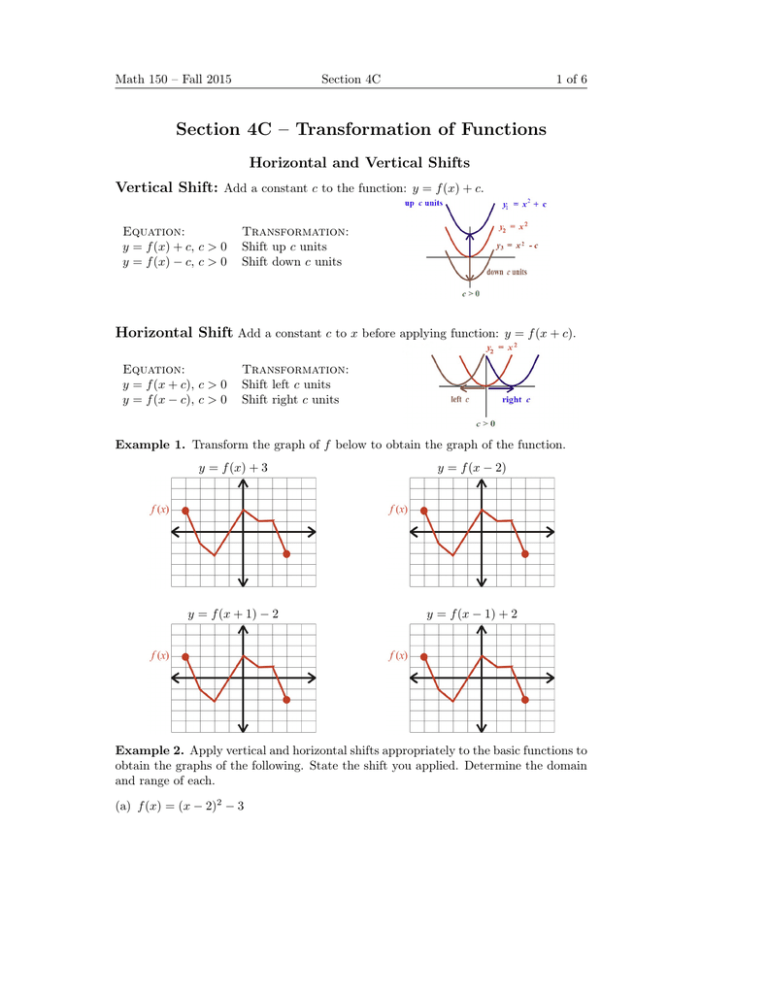



Section 4c Transformation Of Functions Horizontal And Vertical Shifts Vertical Shift
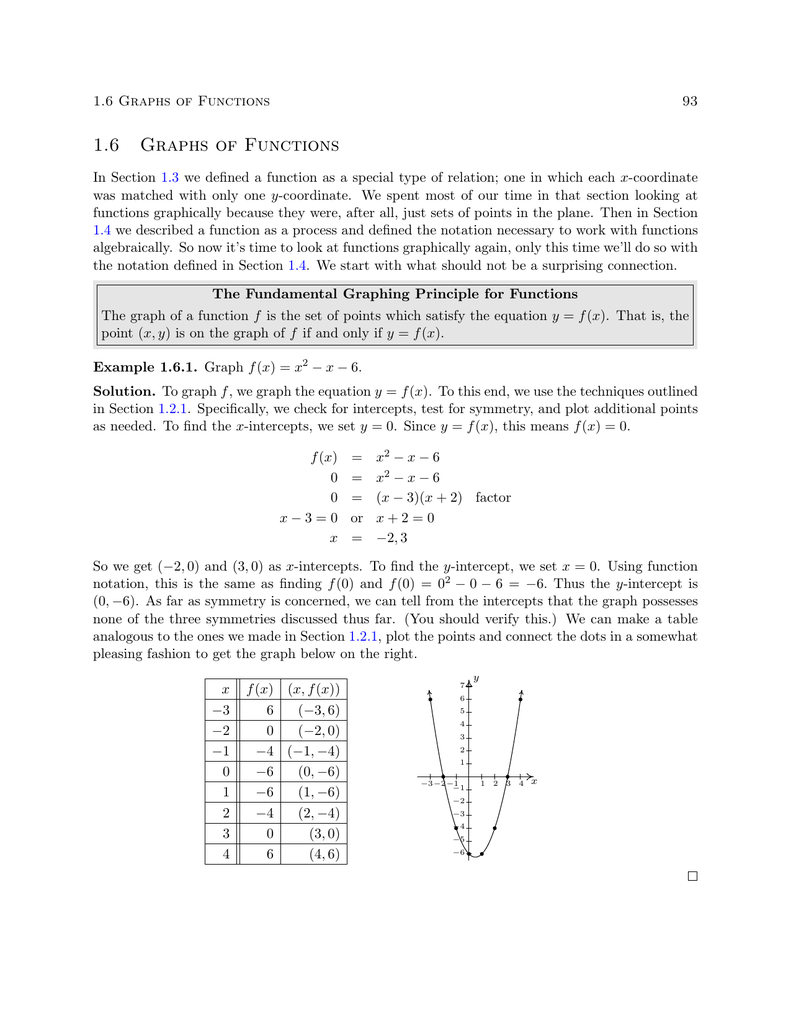



1 6 Graphs Of Functions
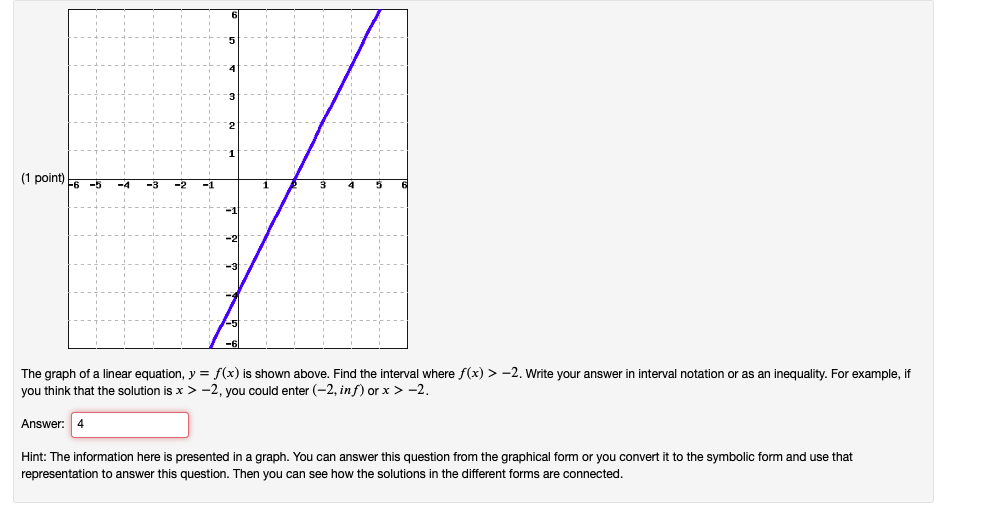



1 Point 6 5 4 The Graph Of A Linear Equation Y Chegg Com
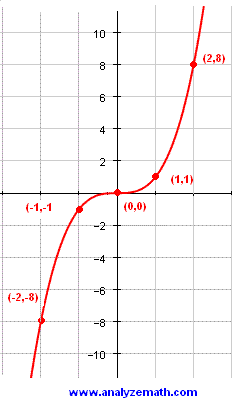



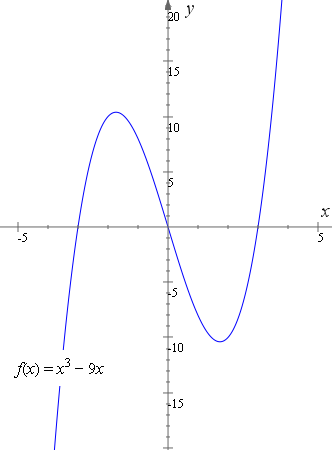
Graphing Cubic Functions
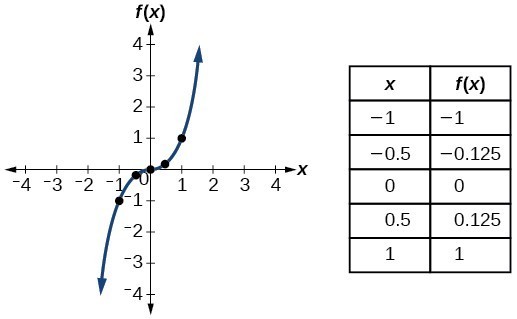



Identify Functions Using Graphs College Algebra



Content Newton S Method




Example 13 Define Function Y F X X 2 Complete The Table




Define The Function F R Gt R By Y F X X 2 X In
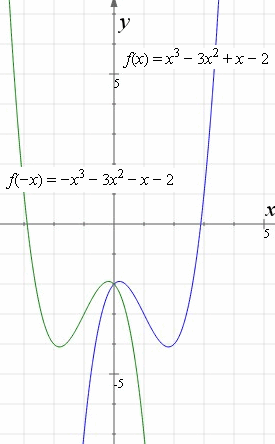



How To Reflect A Graph Through The X Axis Y Axis Or Origin




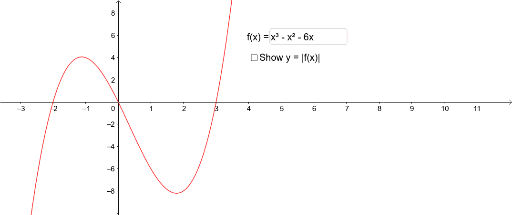
Content Polynomials From Graphs



Integration Area And Curves




Stretching And Reflecting Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation




Transformations Transforming Graphs 7 9 13 Transformations Of Graphs 2 Basic Transformations Restructuring Graphs Vertical Translation F X To F X Ppt Download




Graph Of Y X And Y F X In Example 9 Download Scientific Diagram



Introduction To Limits In Calculus



F X F X 2 F X 2



Reflecting Graphs
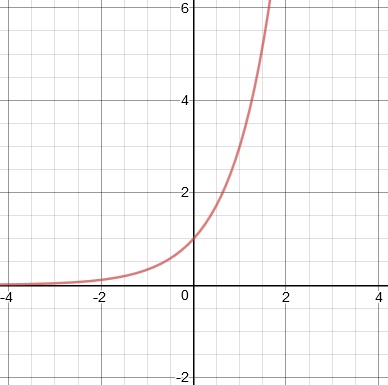



Graphing Exponential Functions




Graph Of Y F X 3 Novocom Top




What Is The Difference Between Y F X And Y F X Quora
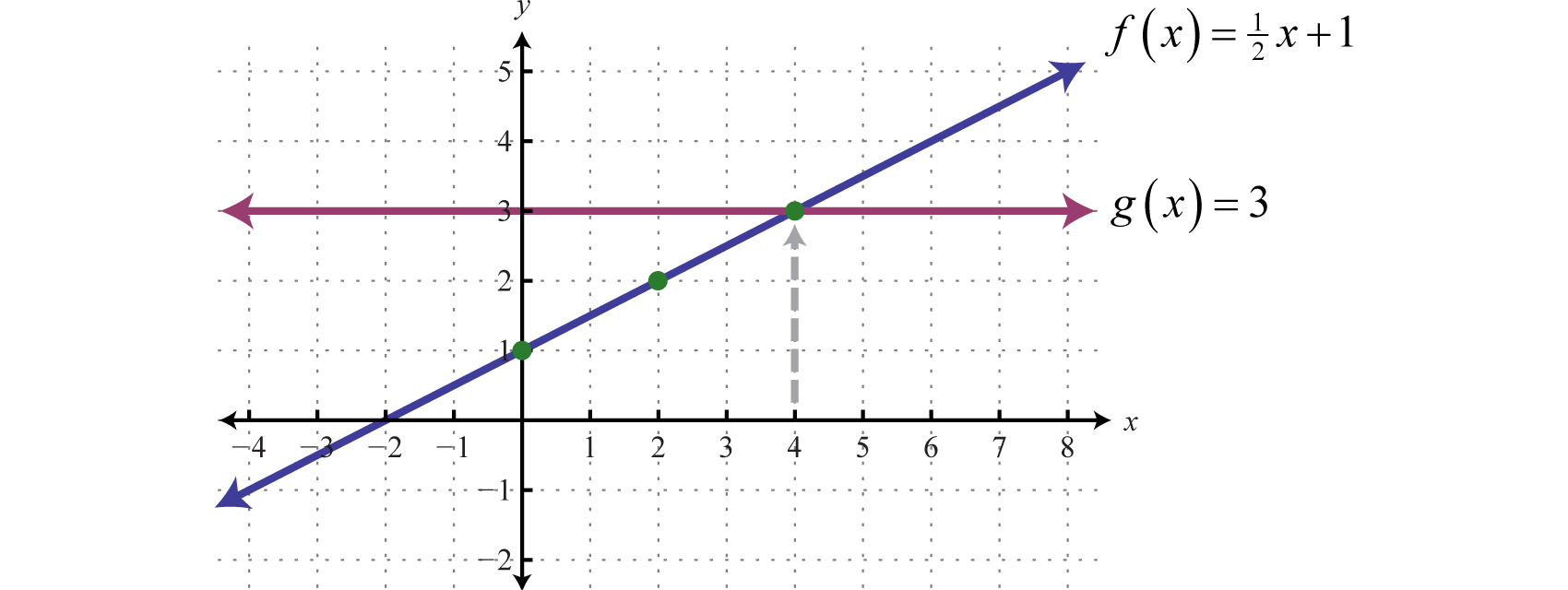



Linear Functions And Their Graphs



One To One Function Explanation Examples



How To Reflect A Graph Through The X Axis Y Axis Or Origin



The Graph Of Y F X Geogebra



Graph The Function Using Transformations Examples



Horizontal Line Test For Function To Have Inverse Expii




Cc Constructing Accurate Graphs Of Antiderivatives
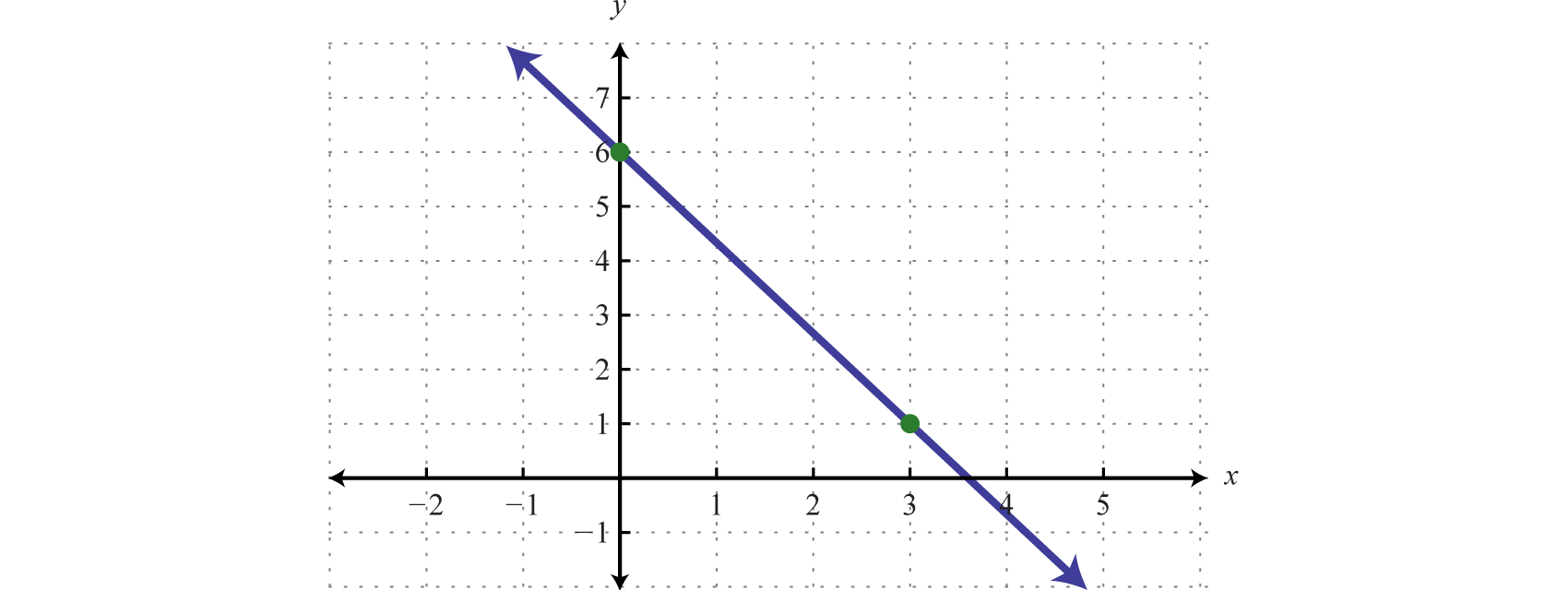



Linear Functions And Their Graphs




End Behavior Of Polynomials Article Khan Academy



Solution How Would F 1 Look On A Graph
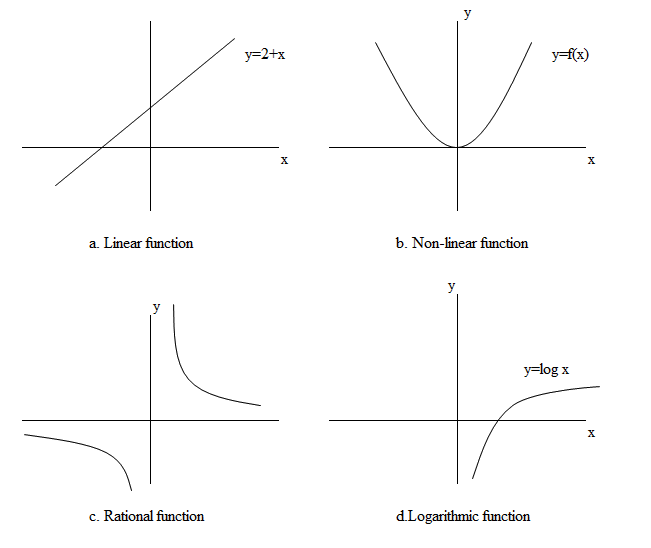



2 Types




Functions And Graphs Aim 1 2 What Are
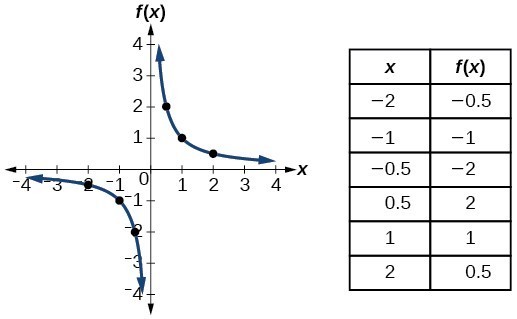



Identify Functions Using Graphs College Algebra




Shifting Of Graphs Transformation Example 1 Y F X Kup K Units Y F X Kdown K Units Vertical Shifting Below Is The Graph Of A Function Y Ppt Download
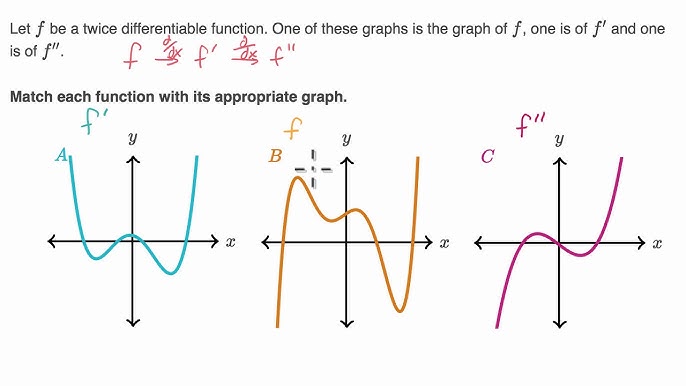



Identifying F F And F Based On Graphs Youtube



Domain And Range
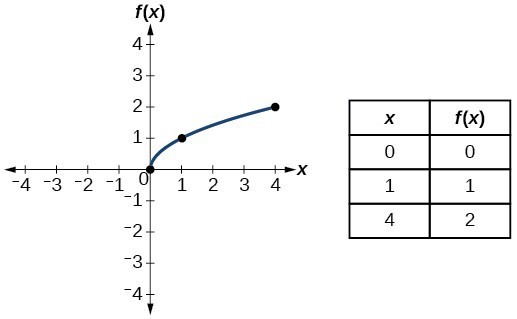



Identify Functions Using Graphs College Algebra
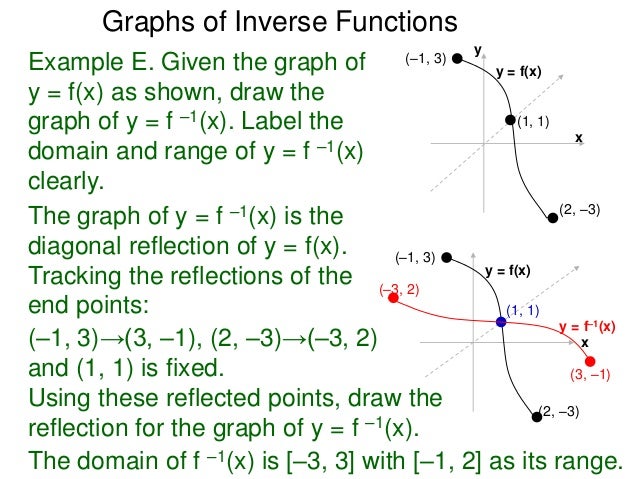



4 1 Inverse Functions



Desmos
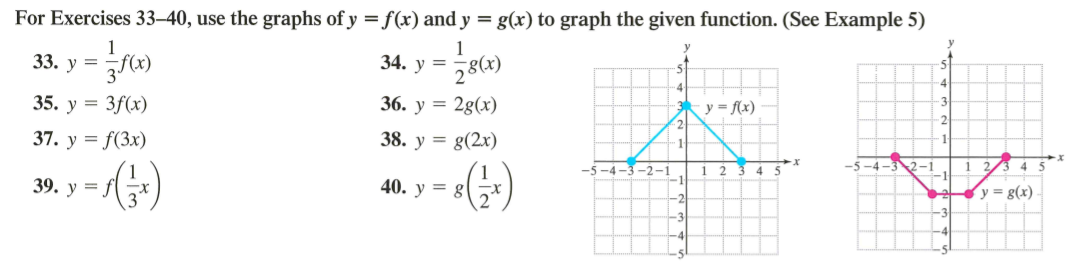



For Exercises 33 40 Use The Graphs Of Y F X And Y Chegg Com




Warm Up How Does The Graph Of Compare To Sketch Both To Confirm Ppt Download
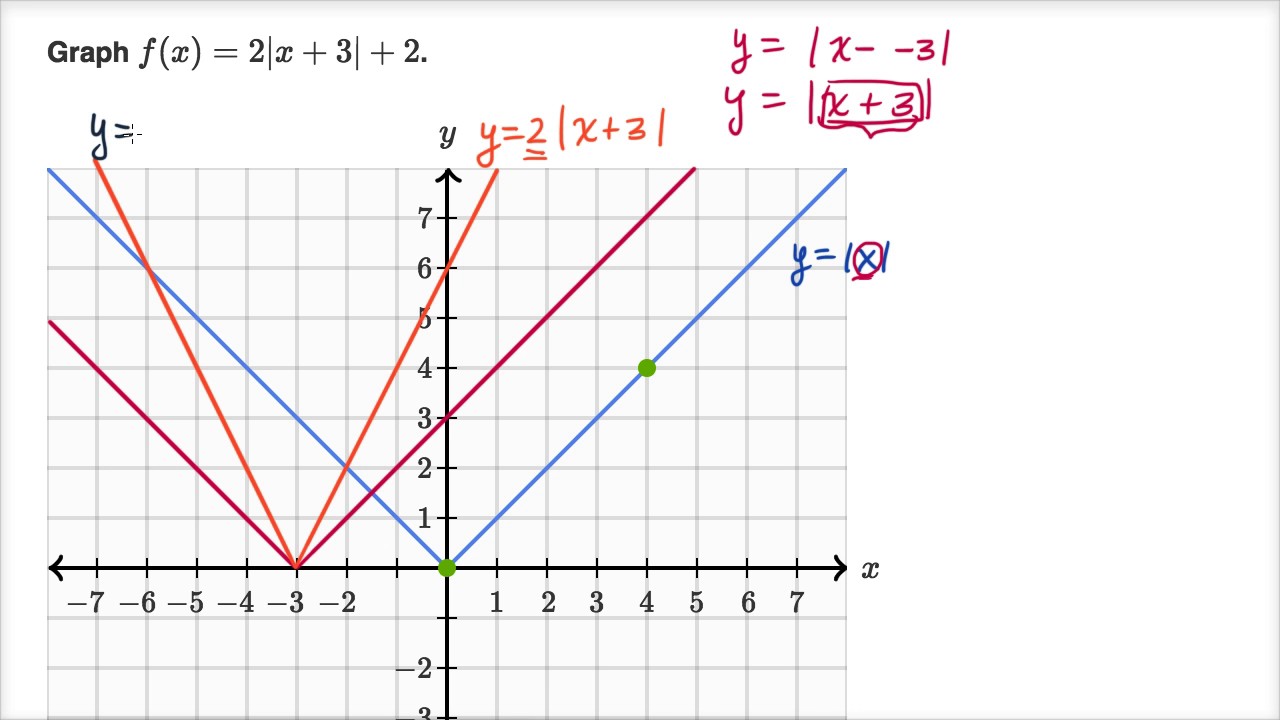



Graphing Absolute Value Functions Video Khan Academy
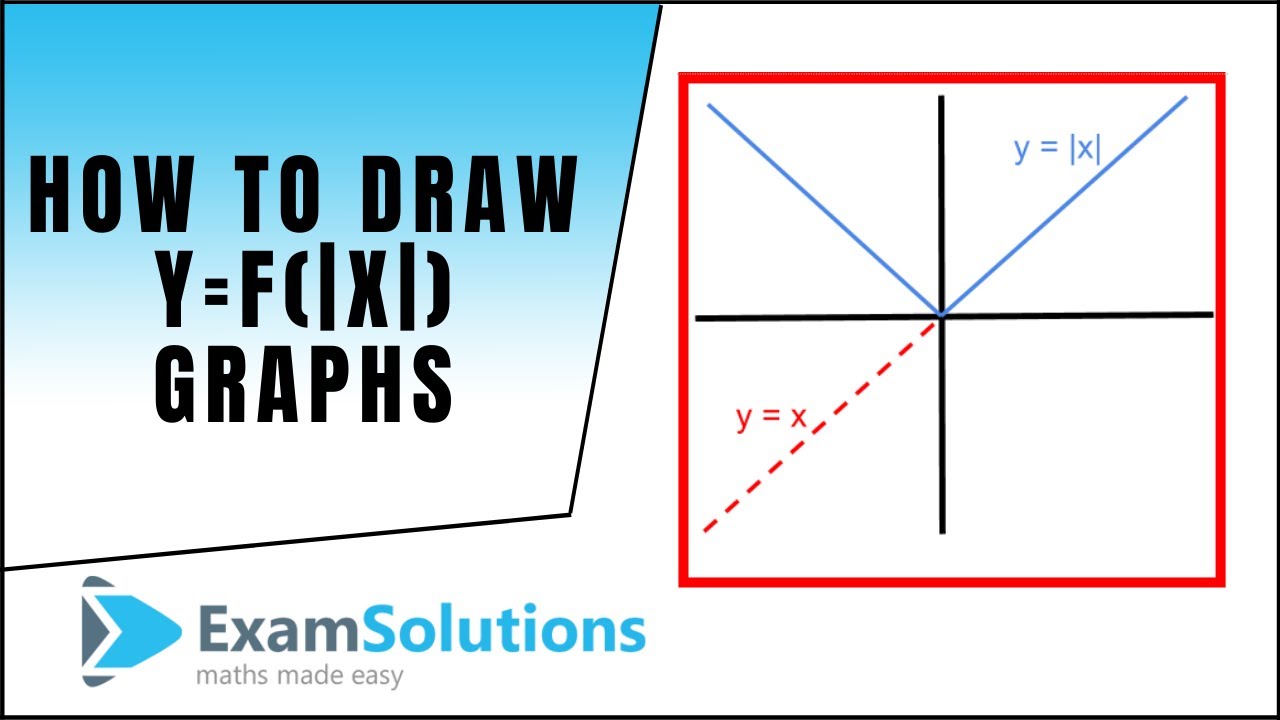



Graphing Y F X Examsolutions




Graphing Reflecting Functions Study Com



Operations On Functions Stretches And Shrinks Sparknotes
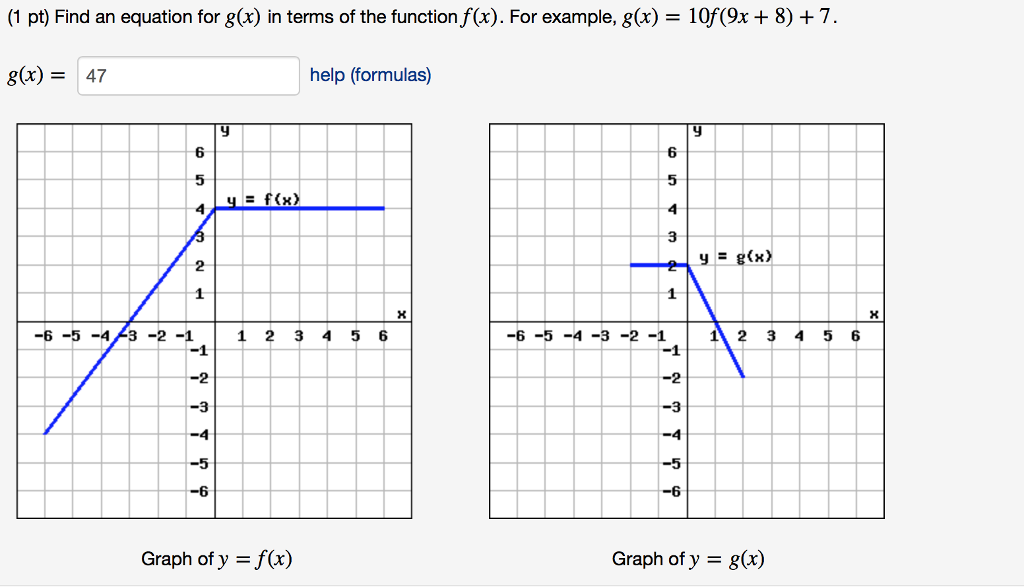



Find An Equation For G X In Terms Of The Function Chegg Com
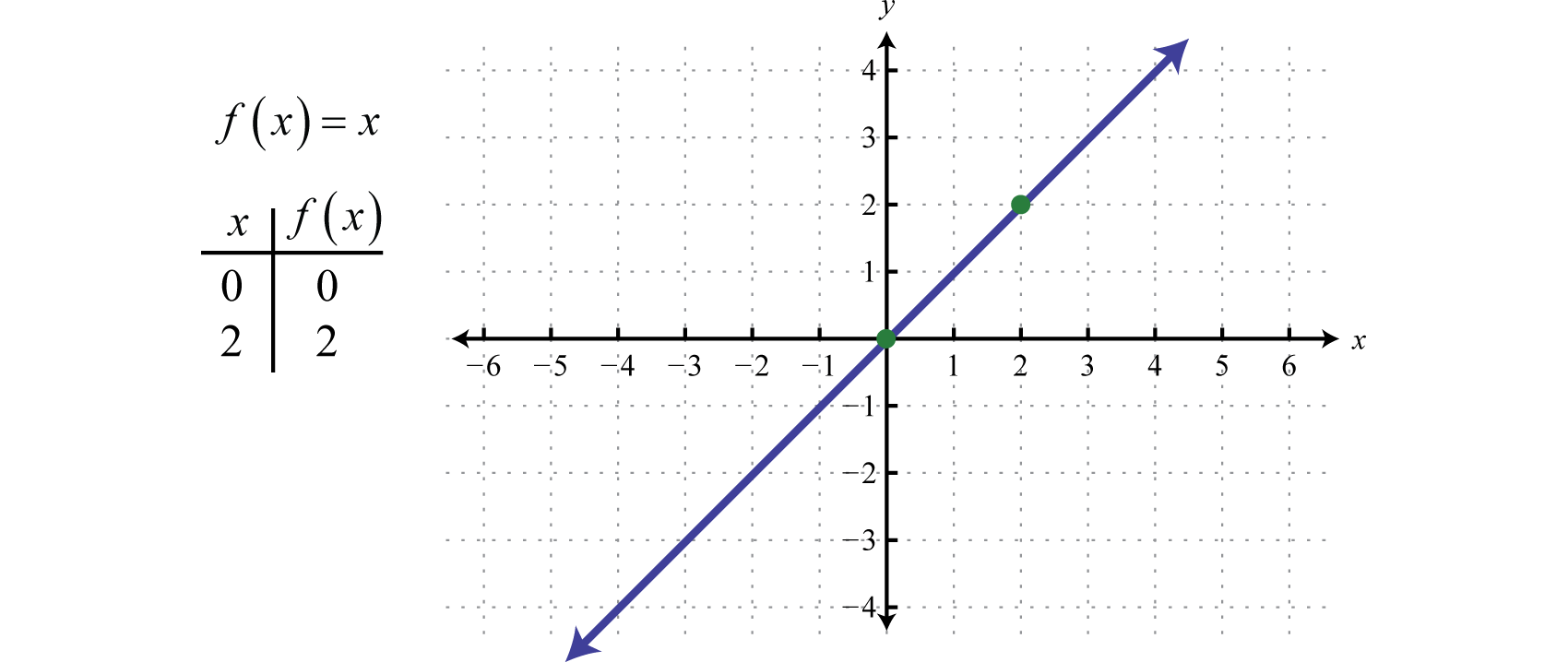



Graphing The Basic Functions




Functions And Graphs Aim 1 2 What Are
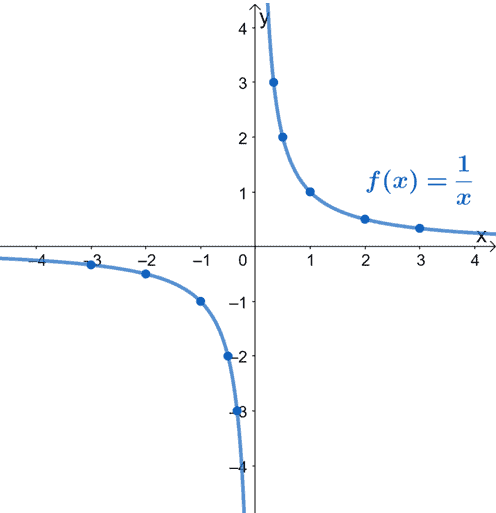



Reciprocal Function Properties Graph And Examples
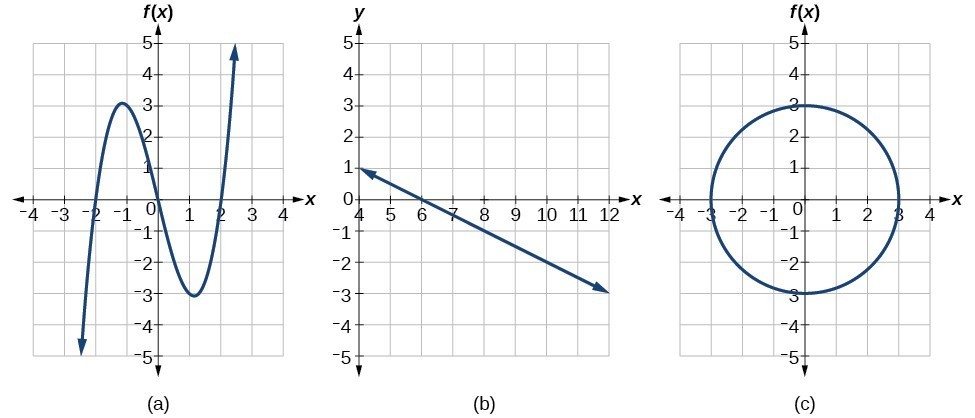



Identify Functions Using Graphs College Algebra




Example Of Area Bounded By Graph Y F X And Limits X A X B And Download Scientific Diagram
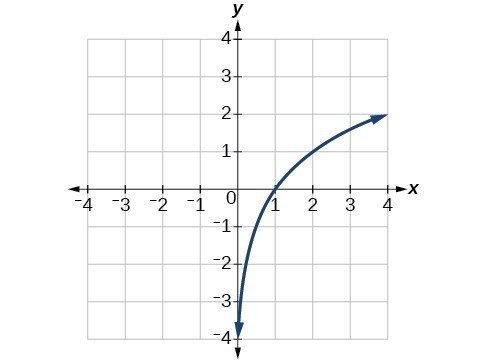



Use The Graph Of A Function To Graph Its Inverse College Algebra




Transforming Exponential Graphs Example 2 Mathematics Iii High School Math Khan Academy Youtube
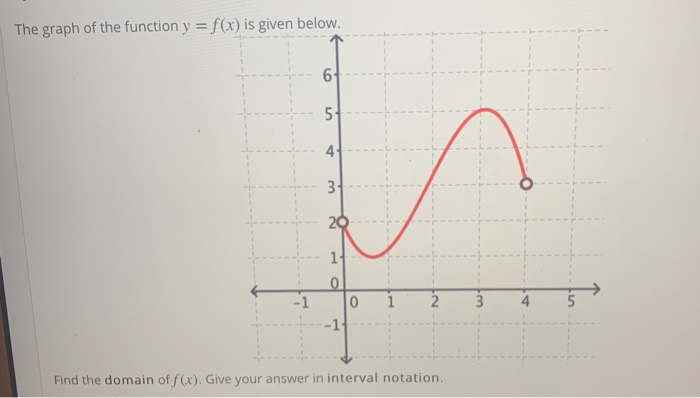



The Graph Of The Function Y F X Is Given Below B Chegg Com



Graph Transformations
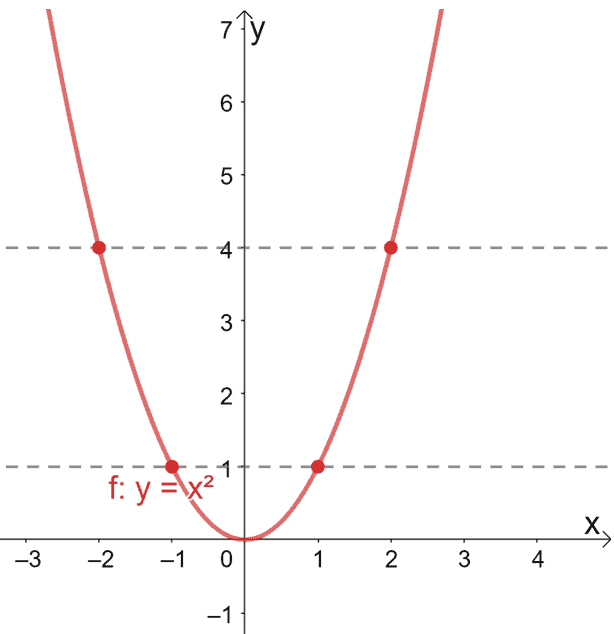



One To One Function Explanation Examples
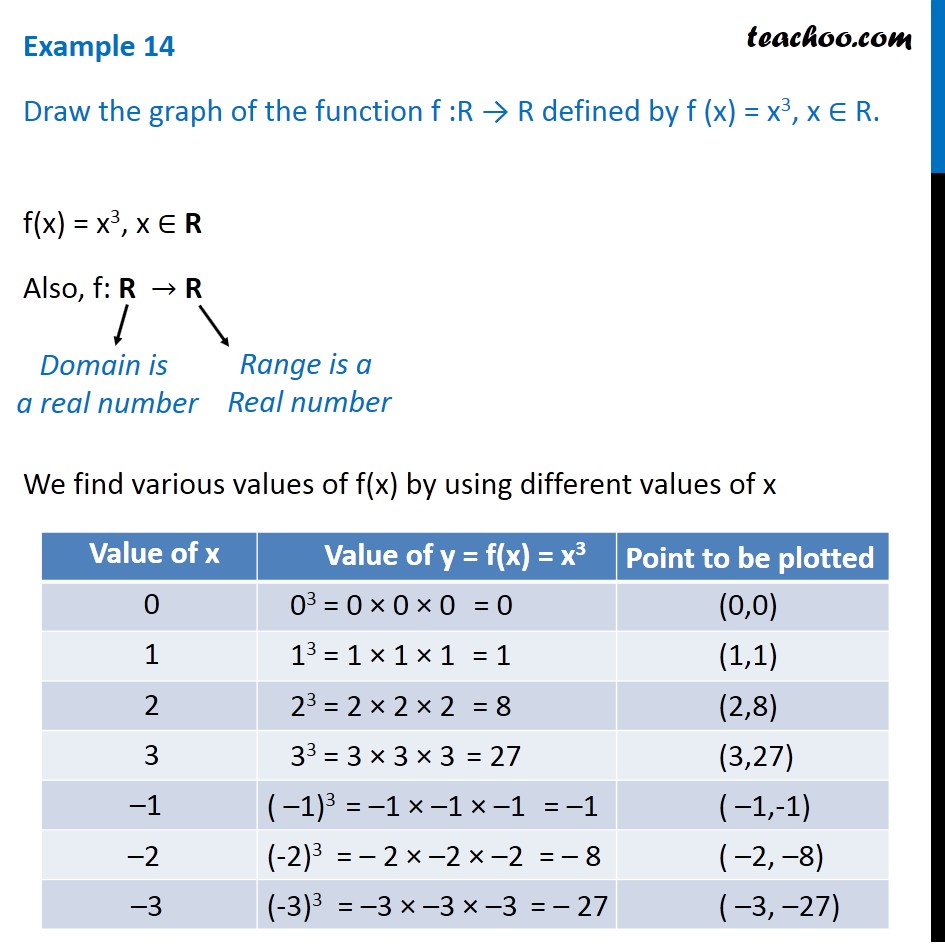



Example 14 Draw Graph Of F X X 3 Chapter 2 Class 11
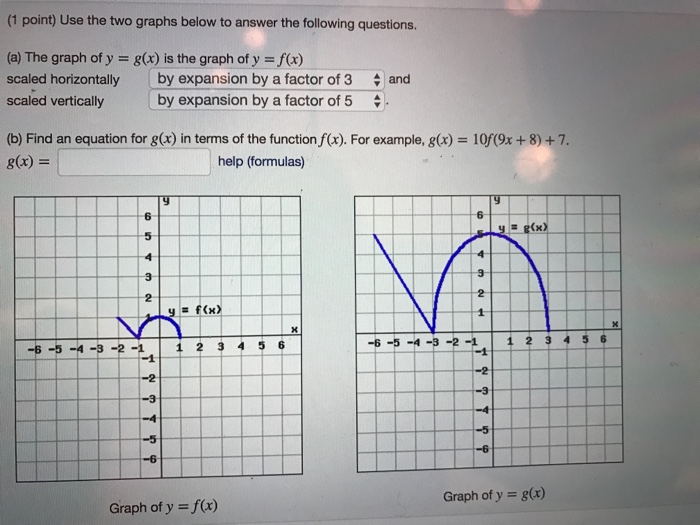



Use The Two Graphs Below To Answer The Following Chegg Com
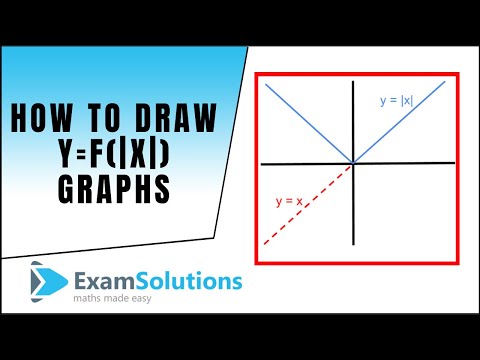



Graphing Y F X Examsolutions


